The invention of Lithium batteries has undoubtedly changed our lives for the better. Lithium batteries are durable under challenging conditions, and hence offer a safe and long-lasting solution to our energy needs. Not only are they the most popular kind of batteries for portable electronics, but they are also used in several other areas such as medical, military, and aerospace. Here we will talk about all you need to know about Lithium batteries and their applications and throw light on the commonly asked questions such as: How many types of lithium batteries are available? How do they charge/discharge? What are the implications on the environment? etc. If you are eager to know more about one of the most remarkable inventions of the 20th century, sit tight and read on!
Experiments with Lithium-ion batteries have been underway since 1912, under American physicist Dr. Gilbert N Lewis, although, they did not hit the commercial market until the 1970s. However, important developments in the area were made in the 1980s when attempts were made to create the first rechargeable battery using lithium as the anode material. After an unfortunate accident in Japan, where a Lithium battery inside a mobile phone exploded, a large number of batteries were recalled from the market, and manufacturers put a higher emphasis on safety measures. However, after extensive research by the American chemist, John B. Goodenough, and Japanese chemists Tokio Yamabe and Shizukuni Yata, a rechargeable and more stable version of the Lithium-ion battery was developed. Sony commercialized the Lithium-ion battery and the three scientists were awarded the Nobel prize for their groundbreaking work.
As the name suggests, lithium-ion batteries use lithium ions to generate electricity. Lithium is a popular choice for batteries because of its high density and lightweight, but it is also one of the most unstable of all metals. Therefore instead of using Lithium directly in the batteries, we use lithium-ions which provide a safer option while retaining the properties of Lithium.
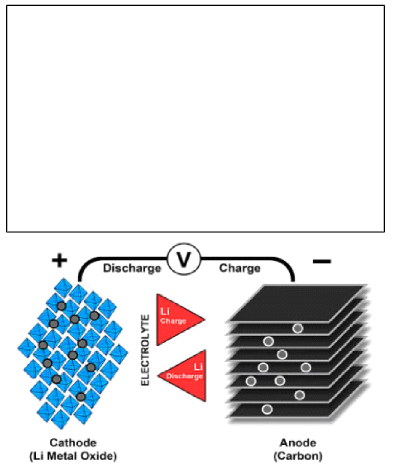
Lithium being the lightest of all metals has the greatest electrochemical potential and provides the largest specific energy per weight. A lithium battery consists of a cathode and anode, along with a separator, electrolyte, and two current collectors one positive and the other negative. The anode and cathode store the lithium. The electrolyte forms the medium through which ions can move from the anode to the cathode and vice versa while passing through a separator. This creates an electric current, which passes through the device being charged to the negative current collector. Meanwhile, the separator obstructs the flow of electrons inside the battery.
During discharge, lithium ions are released from the anode and flow towards the cathode. When the device is charging, the phenomenon reverses itself with the cathode releasing the Lithium ions, to be received by the anode.
Lithium batteries are finding widespread application in various industries, stretching far and beyond mobile phones, and rapidly becoming essential to our day-to-day functioning.
From enabling daily activities to providing emergency support, Here are the major uses for rechargeable lithium batteries–
Types of lithium-ion batteries
The lithium-titanate battery can recharge very quickly, which makes it extremely suitable for electric automobiles and vehicles for public transportation. However, they are susceptible to a lower energy density than other lithium-ion batteries, raising a question mark over their performance. But, they also have a higher density than non-lithium-ion batteries, which forms a silver lining.
Li-Titanate batteries can be used for the construction of smart grids as well as for storing solar and wind energy. Their usage in military and aeronautical systems is also being considered.
Also known as lithium-ion cobalt batteries, they are made from Cobalt and lithium carbonate. These batteries are used in cameras, mobile phones, and laptops owing to their higher specific energy.
Alternatively known as Li-Phosphate batteries, The cathode is made of Phosphate in these batteries. They have a longer lifecycle compared to other Lithium batteries and hence prove to be cost-effective in the long run. They are majorly applied in electric automobiles and other devices which require higher safety standards.
They are also known as li-manganese, manganese spinel batteries, or lithium manganate batteries. The formula was discovered in 1983 and was made commercially viable by Moli Energy in the 1990s. They find widespread use in medical equipment, power tools, laptops, and electric vehicles due to their tolerance to higher temperatures.
Commonly known as NCA batteries, these are being sought out for grid storage and electric vehicles.
Although not suitable for electronic devices, their prospects in the automobile industry are promising. NCA batteries offer a long life span with a higher-energy threshold, but feature behind the other lithium-ion battery types in terms of safety and are heavier on the pocket, and manufacturers need to ensure that NCA batteries are accompanied by monitoring systems. However, they still remain a viable choice for Electric vehicles and might see increased demand in the future.
NMC batteries use a combination of nickel, manganese, and cobalt for their cathode, which is among the most effective ion cathode formulas ever developed. These can serve as Energy Cells or Power Cells, after slight modifications. NMC is the battery of choice for mechanical tools that require additional power sources and electric vehicles.
Sustainability is the need of the hour and hence, it is extremely important to discuss the environmental impacts of energy sources. Lithium batteries find application in Electric vehicles which can greatly contribute to reducing pollution levels in the environment caused by fuel. Lithium batteries contain less toxic metals such as lead or Cadmium and hence are considered to be less hazardous to the environment. However, the mining of Lithium and production of Lithium-ion is quite labor-intensive, and the batteries if not properly recycled, can cause severe impacts on the environment.
The U.S government has built special recycling centers and created specific guidelines for the recycling of lithium batteries in the U.S. These measures if employed by other countries can greatly bring down the adverse effects of the Lithium batteries on the environment. Also, the large reserves of Lithium make it a better alternative to fossil fuels, and shifting more devices, if not all, to lithium-based batteries can provide a temporary solution to environmental pollution.

ARB takes pride in being an internationally certified Lithium-ion battery manufacturer in India.
Copyright © 2022 ARB ACCESSORIES PVT. LTD. All Rights Reserved
Proud Partner | DIBUDDY
Hi